norse.torch.module package¶
Modules for spiking neural network, adhering to the torch.nn.Module interface.
- class norse.torch.module.CobaLIFCell(input_size, hidden_size, p=CobaLIFParameters(tau_syn_exc_inv=tensor(0.2000), tau_syn_inh_inv=tensor(0.2000), c_m_inv=tensor(5.), g_l=tensor(0.2500), e_rev_I=tensor(- 100), e_rev_E=tensor(60), v_rest=tensor(- 20), v_reset=tensor(- 70), v_thresh=tensor(- 10), method='super', alpha=100.0), dt=0.001)[source]¶
Bases:
torch.nn.modules.module.ModuleModule that computes a single euler-integration step of a conductance based LIF neuron-model. More specifically it implements one integration step of the following ODE
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} \dot{v} &= 1/c_{\text{mem}} (g_l (v_{\text{leak}} - v) + g_e (E_{\text{rev_e}} - v) + g_i (E_{\text{rev_i}} - v)) \\ \dot{g_e} &= -1/\tau_{\text{syn}} g_e \\ \dot{g_i} &= -1/\tau_{\text{syn}} g_i \end{align*}\end{split}\]together with the jump condition
\[z = \Theta(v - v_{\text{th}})\]and transition equations
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} v &= (1-z) v + z v_{\text{reset}} \\ g_e &= g_e + \text{relu}(w_{\text{input}}) z_{\text{in}} \\ g_e &= g_e + \text{relu}(w_{\text{rec}}) z_{\text{rec}} \\ g_i &= g_i + \text{relu}(-w_{\text{input}}) z_{\text{in}} \\ g_i &= g_i + \text{relu}(-w_{\text{rec}}) z_{\text{rec}} \\ \end{align*}\end{split}\]where \(z_{\text{rec}}\) and \(z_{\text{in}}\) are the recurrent and input spikes respectively.
- Parameters
input_size (int) – Size of the input.
hidden_size (int) – Size of the hidden state.
p (LIFParameters) – Parameters of the LIF neuron model.
dt (float) – Time step to use.
Examples
>>> batch_size = 16 >>> lif = CobaLIFCell(10, 20) >>> input = torch.randn(batch_size, 10) >>> output, s0 = lif(input)
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- forward(input_tensor, state=None)[source]¶
Defines the computation performed at every call.
Should be overridden by all subclasses.
Note
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the
Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the registered hooks while the latter silently ignores them.- Return type
- class norse.torch.module.CobaLIFParameters(tau_syn_exc_inv: torch.Tensor = tensor(0.2000), tau_syn_inh_inv: torch.Tensor = tensor(0.2000), c_m_inv: torch.Tensor = tensor(5.), g_l: torch.Tensor = tensor(0.2500), e_rev_I: torch.Tensor = tensor(- 100), e_rev_E: torch.Tensor = tensor(60), v_rest: torch.Tensor = tensor(- 20), v_reset: torch.Tensor = tensor(- 70), v_thresh: torch.Tensor = tensor(- 10), method: str = 'super', alpha: float = 100.0)[source]¶
Bases:
tupleParameters of conductance based LIF neuron.
- Parameters
tau_syn_exc_inv (torch.Tensor) – inverse excitatory synaptic input time constant
tau_syn_inh_inv (torch.Tensor) – inverse inhibitory synaptic input time constant
c_m_inv (torch.Tensor) – inverse membrane capacitance
g_l (torch.Tensor) – leak conductance
e_rev_I (torch.Tensor) – inhibitory reversal potential
e_rev_E (torch.Tensor) – excitatory reversal potential
v_rest (torch.Tensor) – rest membrane potential
v_reset (torch.Tensor) – reset membrane potential
v_thresh (torch.Tensor) – threshold membrane potential
method (str) – method to determine the spike threshold (relevant for surrogate gradients)
alpha (float) – hyper parameter to use in surrogate gradient computation
Create new instance of CobaLIFParameters(tau_syn_exc_inv, tau_syn_inh_inv, c_m_inv, g_l, e_rev_I, e_rev_E, v_rest, v_reset, v_thresh, method, alpha)
- c_m_inv: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 2
- e_rev_E: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 5
- e_rev_I: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 4
- g_l: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 3
- tau_syn_exc_inv: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 0
- tau_syn_inh_inv: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 1
- v_reset: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 7
- v_rest: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 6
- v_thresh: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 8
- class norse.torch.module.CobaLIFState(z: torch.Tensor, v: torch.Tensor, g_e: torch.Tensor, g_i: torch.Tensor)[source]¶
Bases:
tupleState of a conductance based LIF neuron.
- Parameters
z (torch.Tensor) – recurrent spikes
v (torch.Tensor) – membrane potential
g_e (torch.Tensor) – excitatory input conductance
g_i (torch.Tensor) – inhibitory input conductance
Create new instance of CobaLIFState(z, v, g_e, g_i)
- g_e: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 2
- g_i: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 3
- v: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 1
- z: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 0
- class norse.torch.module.ConstantCurrentLIFEncoder(seq_length, p=LIFParameters(tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=tensor(100.)), dt=0.001)[source]¶
Bases:
torch.nn.modules.module.ModuleEncodes input currents as fixed (constant) voltage currents, and simulates the spikes that occur during a number of timesteps/iterations (seq_length).
Example
>>> data = torch.as_tensor([2, 4, 8, 16]) >>> seq_length = 2 # Simulate two iterations >>> constant_current_lif_encode(data, seq_length) (tensor([[0.2000, 0.4000, 0.8000, 0.0000], # State in terms of membrane voltage [0.3800, 0.7600, 0.0000, 0.0000]]), tensor([[0., 0., 0., 1.], # Spikes for each iteration [0., 0., 1., 1.]]))
- Parameters
seq_length (int) – The number of iterations to simulate
p (LIFParameters) – Initial neuron parameters.
dt (float) – Time delta between simulation steps
- forward(input_currents)[source]¶
Defines the computation performed at every call.
Should be overridden by all subclasses.
Note
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the
Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the registered hooks while the latter silently ignores them.
- class norse.torch.module.Izhikevich(spiking_method, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNA neuron layer that wraps a
IzhikevichCellin time such that the layer keeps track of temporal sequences of spikes. After application, the layer returns a tuple containing(spikes from all timesteps, state from the last timestep).
Example
>>> data = torch.zeros(10, 5, 2) # 10 timesteps, 5 batches, 2 neurons >>> l = Izhikevich() >>> l(data) # Returns tuple of (Tensor(10, 5, 2), IzhikevichState)
- Parameters
p (IzhikevichParameters) – The neuron parameters as a torch Module, which allows the module to configure neuron parameters as optimizable.
dt (float) – Time step to use in integration. Defaults to 0.001.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.IzhikevichCell(spiking_method, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNCellModule that computes a single Izhikevich neuron-model without recurrence and without time. More specifically it implements one integration step of the following ODE:
\[\begin{align*} \dot{v} &= 0.04v² + 5v + 140 - u + I \dot{u} &= a(bv - u) \end{align*}\]and
\[\text{if} v = 30 \text{mV, then} v = c \text{and} u = u + d\]- Parameters
spiking_method (IzhikevichSpikingBehavior) – parameters and initial state of the neuron
- Example with tonic spiking:
>>> from norse.torch import IzhikevichCell, tonic_spiking >>> batch_size = 16 >>> cell = IzhikevichCell(tonic_spiking) >>> input = torch.randn(batch_size, 10) >>> output, s0 = cell(input)
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.IzhikevichRecurrent(input_size, hidden_size, spiking_method, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNRecurrentA neuron layer that wraps a
IzhikevichRecurrentCellin time such that the layer keeps track of temporal sequences of spikes. After application, the layer returns a tuple containing(spikes from all timesteps, state from the last timestep).
Example
>>> data = torch.zeros(10, 5, 2) # 10 timesteps, 5 batches, 2 neurons >>> l = Izhikevich() >>> l(data) # Returns tuple of (Tensor(10, 5, 2), IzhikevichState)
- Parameters
p (IzhikevichParameters) – The neuron parameters as a torch Module, which allows the module to configure neuron parameters as optimizable.
dt (float) – Time step to use in integration. Defaults to 0.001.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.IzhikevichRecurrentCell(input_size, hidden_size, spiking_method, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNRecurrentCellModule that computes a single euler-integration step of an Izhikevich neuron-model with recurrence but without time. More specifically it implements one integration step of the following ODE :
\[\begin{align*} \dot{v} &= 0.04v² + 5v + 140 - u + I \dot{u} &= a(bv - u) \end{align*}\]and
\[\text{if} v = 30 \text{mV, then} v = c \text{and} u = u + d\]- Example with tonic spiking:
>>> from norse.torch import IzhikevichRecurrentCell, tonic_spiking >>> batch_size = 16 >>> data = torch.zeros(5, 2) # 5 batches, 2 neurons >>> l = IzhikevichRecurrentCell(2, 4) >>> l(data) # Returns tuple of (Tensor(5, 4), IzhikevichState)
- Parameters
input_size (int) – Size of the input. Also known as the number of input features. Defaults to None
hidden_size (int) – Size of the hidden state. Also known as the number of input features. Defaults to None
p (IzhikevichParameters) – Parameters of the Izhikevich neuron model.
input_weights (torch.Tensor) – Weights used for input tensors. Defaults to a random matrix normalized to the number of hidden neurons.
recurrent_weights (torch.Tensor) – Weights used for input tensors. Defaults to a random matrix normalized to the number of hidden neurons.
autapses (bool) – Allow self-connections in the recurrence? Defaults to False. Will also remove autapses in custom recurrent weights, if set above.
dt (float) – Time step to use. Defaults to 0.001.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.LConv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, device=None, dtype=None)[source]¶
Bases:
torch.nn.modules.conv.Conv3dImplements a 2d-convolution applied pointwise in time. See https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Conv2d.html?highlight=conv2d#torch.nn.Conv2d, for documentation of the arguments, which we will reproduce in part here.
This module expects an additional temporal dimension in the tensor it is passed, that is in the notation in the documentation referenced above, it turns in the simplest case a tensor with input shape \((T, N, C_{ ext{in}}, H, W)\) and output tensor of shape \((T, N, C_{ ext{out}}, H_{ ext{out}}, W_{ ext{out}})\), by applying a 2d convolution operation pointwise along the time-direction, with T denoting the number of time steps.
{groups_note}
- The parameters
kernel_size,stride,padding,dilationcan either be: a single
int– in which case the same value is used for the height and width dimensiona
tupleof two ints – in which case, the first int is used for the height dimension, and the second int for the width dimension
- Parameters
in_channels (int) – Number of channels in the input image
out_channels (int) – Number of channels produced by the convolution
stride (int or tuple, optional) – Stride of the convolution. Default: 1
padding (int, tuple or str, optional) – Padding added to all four sides of the input. Default: 0
dilation (int or tuple, optional) – Spacing between kernel elements. Default: 1
groups (int, optional) – Number of blocked connections from input channels to output channels. Default: 1
- bias: Optional[torch.Tensor]¶
- forward(input_tensor)[source]¶
Defines the computation performed at every call.
Should be overridden by all subclasses.
Note
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the
Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the registered hooks while the latter silently ignores them.
- weight: torch.Tensor¶
- The parameters
- class norse.torch.module.LICell(p=LIParameters(tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.)), **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNCellCell for a leaky-integrator without recurrence. More specifically it implements a discretized version of the ODE
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} \dot{v} &= 1/\tau_{\text{mem}} (v_{\text{leak}} - v + i) \\ \dot{i} &= -1/\tau_{\text{syn}} i \end{align*}\end{split}\]and transition equations
\[i = i + w i_{\text{in}}\]- Parameters
p (LIParameters) – parameters of the leaky integrator
dt (float) – integration timestep to use
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.LIF(p=LIFParameters(tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=tensor(100.)), **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNA neuron layer that wraps a
LIFCellin time such that the layer keeps track of temporal sequences of spikes. After application, the layer returns a tuple containing(spikes from all timesteps, state from the last timestep).
Example
>>> data = torch.zeros(10, 5, 2) # 10 timesteps, 5 batches, 2 neurons >>> l = LIF() >>> l(data) # Returns tuple of (Tensor(10, 5, 2), LIFState)
- Parameters
p (LIFParameters) – The neuron parameters as a torch Module, which allows the module to configure neuron parameters as optimizable.
sparse (bool) – Whether to apply sparse activation functions (True) or not (False). Defaults to False.
dt (float) – Time step to use in integration. Defaults to 0.001.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.LIFAdEx(p=LIFAdExParameters(adaptation_current=tensor(4), adaptation_spike=tensor(0.0200), delta_T=tensor(0.5000), tau_ada_inv=tensor(2.), tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=100.0), **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNA neuron layer that wraps a recurrent LIFAdExCell in time such that the layer keeps track of temporal sequences of spikes. After application, the layer returns a tuple containing
(spikes from all timesteps, state from the last timestep).
Example
>>> data = torch.zeros(10, 5, 2) # 10 timesteps, 5 batches, 2 neurons >>> l = LIFAdExLayer(2, 4) >>> l(data) # Returns tuple of (Tensor(10, 5, 4), LIFExState)
- Parameters
p (LIFAdExParameters) – The neuron parameters as a torch Module, which allows the module to configure neuron parameters as optimizable.
dt (float) – Time step to use in integration. Defaults to 0.001.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.LIFAdExCell(p=LIFAdExParameters(adaptation_current=tensor(4), adaptation_spike=tensor(0.0200), delta_T=tensor(0.5000), tau_ada_inv=tensor(2.), tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=100.0), **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNCellComputes a single euler-integration step of a feed-forward exponential LIF neuron-model without recurrence, adapted from http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/Adaptive_exponential_integrate-and-fire_model. It takes as input the input current as generated by an arbitrary torch module or function. More specifically it implements one integration step of the following ODE
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} \dot{v} &= 1/\tau_{\text{mem}} \left(v_{\text{leak}} - v + i + \Delta_T exp\left({{v - v_{\text{th}}} \over {\Delta_T}}\right)\right) \\ \dot{i} &= -1/\tau_{\text{syn}} i \\ \dot{a} &= 1/\tau_{\text{ada}} \left( a_{current} (V - v_{\text{leak}}) - a \right) \end{align*}\end{split}\]together with the jump condition
\[z = \Theta(v - v_{\text{th}})\]and transition equations
\[i = i + i_{\text{in}}\]where \(i_{\text{in}}\) is meant to be the result of applying an arbitrary pytorch module (such as a convolution) to input spikes.
- Parameters
p (LIFAdExParameters) – Parameters of the LIFEx neuron model.
dt (float) – Time step to use.
Examples
>>> batch_size = 16 >>> lif_ex = LIFAdExCell() >>> data = torch.randn(batch_size, 20, 30) >>> output, s0 = lif_ex(data)
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.LIFAdExFeedForwardState(v: torch.Tensor, i: torch.Tensor, a: torch.Tensor)[source]¶
Bases:
tupleState of a feed forward LIFAdEx neuron
- Parameters
v (torch.Tensor) – membrane potential
i (torch.Tensor) – synaptic input current
a (torch.Tensor) – membrane potential adaptation factor
Create new instance of LIFAdExFeedForwardState(v, i, a)
- a: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 2
- i: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 1
- v: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 0
- class norse.torch.module.LIFAdExParameters(adaptation_current: torch.Tensor = tensor(4), adaptation_spike: torch.Tensor = tensor(0.0200), delta_T: torch.Tensor = tensor(0.5000), tau_ada_inv: torch.Tensor = tensor(2.), tau_syn_inv: torch.Tensor = tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv: torch.Tensor = tensor(100.), v_leak: torch.Tensor = tensor(0.), v_th: torch.Tensor = tensor(1.), v_reset: torch.Tensor = tensor(0.), method: str = 'super', alpha: float = 100.0)[source]¶
Bases:
tupleParametrization of an Adaptive Exponential Leaky Integrate and Fire neuron
Default values from https://github.com/NeuralEnsemble/PyNN/blob/d8056fa956998b031a1c3689a528473ed2bc0265/pyNN/standardmodels/cells.py#L416
- Parameters
adaptation_current (torch.Tensor) – adaptation coupling parameter in nS
adaptation_spike (torch.Tensor) – spike triggered adaptation parameter in nA
delta_T (torch.Tensor) – sharpness or speed of the exponential growth in mV
tau_syn_inv (torch.Tensor) – inverse adaptation time constant (\(1/\tau_\text{ada}\)) in 1/ms
tau_syn_inv – inverse synaptic time constant (\(1/\tau_\text{syn}\)) in 1/ms
tau_mem_inv (torch.Tensor) – inverse membrane time constant (\(1/\tau_\text{mem}\)) in 1/ms
v_leak (torch.Tensor) – leak potential in mV
v_th (torch.Tensor) – threshold potential in mV
v_reset (torch.Tensor) – reset potential in mV
method (str) – method to determine the spike threshold (relevant for surrogate gradients)
alpha (float) – hyper parameter to use in surrogate gradient computation
Create new instance of LIFAdExParameters(adaptation_current, adaptation_spike, delta_T, tau_ada_inv, tau_syn_inv, tau_mem_inv, v_leak, v_th, v_reset, method, alpha)
- adaptation_current: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 0
- adaptation_spike: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 1
- delta_T: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 2
- tau_ada_inv: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 3
- tau_mem_inv: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 5
- tau_syn_inv: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 4
- v_leak: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 6
- v_reset: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 8
- v_th: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 7
- class norse.torch.module.LIFAdExRecurrent(input_size, hidden_size, p=LIFAdExParameters(adaptation_current=tensor(4), adaptation_spike=tensor(0.0200), delta_T=tensor(0.5000), tau_ada_inv=tensor(2.), tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=100.0), **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNRecurrentA neuron layer that wraps a recurrent LIFAdExRecurrentCell in time (with recurrence) such that the layer keeps track of temporal sequences of spikes. After application, the layer returns a tuple containing
(spikes from all timesteps, state from the last timestep).
Example
>>> data = torch.zeros(10, 5, 2) # 10 timesteps, 5 batches, 2 neurons >>> l = LIFAdExRecurrent(2, 4) >>> l(data) # Returns tuple of (Tensor(10, 5, 4), LIFAdExState)
- Parameters
input_size (int) – The number of input neurons
hidden_size (int) – The number of hidden neurons
p (LIFAdExParameters) – The neuron parameters as a torch Module, which allows the module to configure neuron parameters as optimizable.
input_weights (torch.Tensor) – Weights used for input tensors. Defaults to a random matrix normalized to the number of hidden neurons.
recurrent_weights (torch.Tensor) – Weights used for input tensors. Defaults to a random matrix normalized to the number of hidden neurons.
autapses (bool) – Allow self-connections in the recurrence? Defaults to False. Will also remove autapses in custom recurrent weights, if set above.
dt (float) – Time step to use in integration. Defaults to 0.001.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.LIFAdExRecurrentCell(input_size, hidden_size, p=LIFAdExParameters(adaptation_current=tensor(4), adaptation_spike=tensor(0.0200), delta_T=tensor(0.5000), tau_ada_inv=tensor(2.), tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=100.0), **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNRecurrentCellComputes a single of euler-integration step of a recurrent adaptive exponential LIF neuron-model with recurrence, adapted from http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/Adaptive_exponential_integrate-and-fire_model. More specifically it implements one integration step of the following ODE
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} \dot{v} &= 1/\tau_{\text{mem}} \left(v_{\text{leak}} - v + i + \Delta_T exp\left({{v - v_{\text{th}}} \over {\Delta_T}}\right)\right) \\ \dot{i} &= -1/\tau_{\text{syn}} i \\ \dot{a} &= 1/\tau_{\text{ada}} \left( a_{current} (V - v_{\text{leak}}) - a \right) \end{align*}\end{split}\]together with the jump condition
\[z = \Theta(v - v_{\text{th}})\]and transition equations
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} v &= (1-z) v + z v_{\text{reset}} \\ i &= i + w_{\text{input}} z_{\text{in}} \\ i &= i + w_{\text{rec}} z_{\text{rec}} \end{align*}\end{split}\]where \(z_{\text{rec}}\) and \(z_{\text{in}}\) are the recurrent and input spikes respectively.
Examples
>>> batch_size = 16 >>> lif = LIFAdExRecurrentCell(10, 20) >>> input = torch.randn(batch_size, 10) >>> output, s0 = lif(input)
- Parameters
input_size (int) – Size of the input. Also known as the number of input features.
hidden_size (int) – Size of the hidden state. Also known as the number of input features.
p (LIFAdExParameters) – Parameters of the LIF neuron model.
input_weights (torch.Tensor) – Weights used for input tensors. Defaults to a random matrix normalized to the number of hidden neurons.
recurrent_weights (torch.Tensor) – Weights used for input tensors. Defaults to a random matrix normalized to the number of hidden neurons.
autapses (bool) – Allow self-connections in the recurrence? Defaults to False. Will also remove autapses in custom recurrent weights, if set above.
dt (float) – Time step to use.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.LIFAdExState(z: torch.Tensor, v: torch.Tensor, i: torch.Tensor, a: torch.Tensor)[source]¶
Bases:
tupleState of a LIFAdEx neuron
- Parameters
z (torch.Tensor) – recurrent spikes
v (torch.Tensor) – membrane potential
i (torch.Tensor) – synaptic input current
a (torch.Tensor) – membrane potential adaptation factor
Create new instance of LIFAdExState(z, v, i, a)
- a: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 3
- i: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 2
- v: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 1
- z: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 0
- class norse.torch.module.LIFCell(p=LIFParameters(tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=tensor(100.)), **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNCellModule that computes a single euler-integration step of a leaky integrate-and-fire (LIF) neuron-model without recurrence and without time.
More specifically it implements one integration step of the following ODE
\[\begin{align*} \dot{v} &= 1/\tau_{\text{mem}} (v_{\text{leak}} - v + i) \ \dot{i} &= -1/\tau_{\text{syn}} i \end{align*}\]together with the jump condition
\[z = \Theta(v - v_{\text{th}})\]and transition equations
\[\begin{align*} v &= (1-z) v + z v_{\text{reset}} \end{align*}\]Example
>>> data = torch.zeros(5, 2) # 5 batches, 2 neurons >>> l = LIFCell(2, 4) >>> l(data) # Returns tuple of (Tensor(5, 4), LIFState)
- Parameters
p (LIFParameters) – Parameters of the LIF neuron model.
sparse (bool) – Whether to apply sparse activation functions (True) or not (False). Defaults to False.
dt (float) – Time step to use. Defaults to 0.001.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.LIFCorrelation(input_size, hidden_size, p=LIFCorrelationParameters(lif_parameters=LIFParameters(tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=tensor(100.)), input_correlation_parameters=CorrelationSensorParameters(eta_p=tensor(1.), eta_m=tensor(1.), tau_ac_inv=tensor(10.), tau_c_inv=tensor(10.)), recurrent_correlation_parameters=CorrelationSensorParameters(eta_p=tensor(1.), eta_m=tensor(1.), tau_ac_inv=tensor(10.), tau_c_inv=tensor(10.))), dt=0.001)[source]¶
Bases:
torch.nn.modules.module.ModuleInitializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- forward(input_tensor, input_weights, recurrent_weights, state)[source]¶
Defines the computation performed at every call.
Should be overridden by all subclasses.
Note
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the
Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the registered hooks while the latter silently ignores them.- Return type
- class norse.torch.module.LIFCorrelationParameters(lif_parameters, input_correlation_parameters, recurrent_correlation_parameters)[source]¶
Bases:
tupleCreate new instance of LIFCorrelationParameters(lif_parameters, input_correlation_parameters, recurrent_correlation_parameters)
- input_correlation_parameters: norse.torch.functional.correlation_sensor.CorrelationSensorParameters¶
Alias for field number 1
- lif_parameters: norse.torch.functional.lif.LIFParameters¶
Alias for field number 0
- recurrent_correlation_parameters: norse.torch.functional.correlation_sensor.CorrelationSensorParameters¶
Alias for field number 2
- class norse.torch.module.LIFCorrelationState(lif_state, input_correlation_state, recurrent_correlation_state)[source]¶
Bases:
tupleCreate new instance of LIFCorrelationState(lif_state, input_correlation_state, recurrent_correlation_state)
- input_correlation_state: norse.torch.functional.correlation_sensor.CorrelationSensorState¶
Alias for field number 1
- lif_state: norse.torch.functional.lif.LIFState¶
Alias for field number 0
- recurrent_correlation_state: norse.torch.functional.correlation_sensor.CorrelationSensorState¶
Alias for field number 2
- class norse.torch.module.LIFEx(p=LIFExParameters(delta_T=tensor(0.5000), tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=100.0), **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNA neuron layer that wraps a
LIFExCellin time such that the layer keeps track of temporal sequences of spikes. After application, the layer returns a tuple containing(spikes from all timesteps, state from the last timestep).
Example
>>> data = torch.zeros(10, 5, 2) # 10 timesteps, 5 batches, 2 neurons >>> l = LIFEx() >>> l(data) # Returns tuple of (Tensor(10, 5, 2), LIFExState)
- Parameters
p (LIFExParameters) – The neuron parameters as a torch Module, which allows the module to configure neuron parameters as optimizable. Defaults to None.
dt (float) – Time step to use in integration. Defaults to 0.001.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.LIFExCell(p=LIFExParameters(delta_T=tensor(0.5000), tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=100.0), **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNCellComputes a single euler-integration step of a recurrent exponential LIF neuron-model (without recurrence) adapted from https://neuronaldynamics.epfl.ch/online/Ch5.S2.html. More specifically it implements one integration step of the following ODE
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} \dot{v} &= 1/\tau_{\text{mem}} \left(v_{\text{leak}} - v + i + \Delta_T exp\left({{v - v_{\text{th}}} \over {\Delta_T}}\right)\right) \\ \dot{i} &= -1/\tau_{\text{syn}} i \end{align*}\end{split}\]together with the jump condition
\[z = \Theta(v - v_{\text{th}})\]and transition equations
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} v &= (1-z) v + z v_{\\text{reset}} \end{align*}\end{split}\]where \(z_{\text{rec}}\) and \(z_{\text{in}}\) are the recurrent and input spikes respectively.
- Parameters
input_size (int) – Size of the input.
hidden_size (int) – Size of the hidden state.
p (LIFExParameters) – Parameters of the LIF neuron model.
dt (float) – Time step to use.
autapses (bool) – Allow self-connections in the recurrence? Defaults to False.
Examples
>>> batch_size = 16 >>> lif_ex = LIFExCell(10, 20) >>> input = torch.randn(batch_size, 10) >>> output, s0 = lif_ex(input)
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.LIFExFeedForwardState(v: torch.Tensor, i: torch.Tensor)[source]¶
Bases:
tupleState of a feed forward LIFEx neuron
- Parameters
v (torch.Tensor) – membrane potential
i (torch.Tensor) – synaptic input current
Create new instance of LIFExFeedForwardState(v, i)
- i: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 1
- v: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 0
- class norse.torch.module.LIFExParameters(delta_T: torch.Tensor = tensor(0.5000), tau_syn_inv: torch.Tensor = tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv: torch.Tensor = tensor(100.), v_leak: torch.Tensor = tensor(0.), v_th: torch.Tensor = tensor(1.), v_reset: torch.Tensor = tensor(0.), method: str = 'super', alpha: float = 100.0)[source]¶
Bases:
tupleParametrization of an Exponential Leaky Integrate and Fire neuron
- Parameters
delta_T (torch.Tensor) – sharpness or speed of the exponential growth in mV
tau_syn_inv (torch.Tensor) – inverse synaptic time constant (\(1/\tau_\text{syn}\)) in 1/ms
tau_mem_inv (torch.Tensor) – inverse membrane time constant (\(1/\tau_\text{mem}\)) in 1/ms
v_leak (torch.Tensor) – leak potential in mV
v_th (torch.Tensor) – threshold potential in mV
v_reset (torch.Tensor) – reset potential in mV
method (str) – method to determine the spike threshold (relevant for surrogate gradients)
alpha (float) – hyper parameter to use in surrogate gradient computation
Create new instance of LIFExParameters(delta_T, tau_syn_inv, tau_mem_inv, v_leak, v_th, v_reset, method, alpha)
- delta_T: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 0
- tau_mem_inv: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 2
- tau_syn_inv: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 1
- v_leak: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 3
- v_reset: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 5
- v_th: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 4
- class norse.torch.module.LIFExRecurrent(input_size, hidden_size, p=LIFExParameters(delta_T=tensor(0.5000), tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=100.0), **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNRecurrentA neuron layer that wraps a
LIFExRecurrentCellin time such that the layer keeps track of temporal sequences of spikes. After application, the module returns a tuple containing(spikes from all timesteps, state from the last timestep).
Example
>>> data = torch.zeros(10, 5, 2) # 10 timesteps, 5 batches, 2 neurons >>> l = LIFExRecurrent(2, 4) >>> l(data) # Returns tuple of (Tensor(10, 5, 4), LIFExState)
- Parameters
input_size (int) – The number of input neurons
hidden_size (int) – The number of hidden neurons
p (LIFExParameters) – The neuron parameters as a torch Module, which allows the module to configure neuron parameters as optimizable. Defaults to None.
input_weights (torch.Tensor) – Weights used for input tensors. Defaults to a random matrix normalized to the number of hidden neurons.
recurrent_weights (torch.Tensor) – Weights used for input tensors. Defaults to a random matrix normalized to the number of hidden neurons.
autapses (bool) – Allow self-connections in the recurrence? Defaults to False. Will also remove autapses in custom recurrent weights, if set above.
dt (float) – Time step to use in integration. Defaults to 0.001.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.LIFExRecurrentCell(input_size, hidden_size, p=LIFExParameters(delta_T=tensor(0.5000), tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=100.0), **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNRecurrentCellComputes a single euler-integration step of a recurrent exponential LIFEx neuron-model (with recurrence) adapted from https://neuronaldynamics.epfl.ch/online/Ch5.S2.html. More specifically it implements one integration step of the following ODE
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} \dot{v} &= 1/\tau_{\text{mem}} \left(v_{\text{leak}} - v + i + \Delta_T exp\left({{v - v_{\text{th}}} \over {\Delta_T}}\right)\right) \\ \dot{i} &= -1/\tau_{\text{syn}} i \end{align*}\end{split}\]together with the jump condition
\[z = \Theta(v - v_{\text{th}})\]and transition equations
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} v &= (1-z) v + z v_{\\text{reset}} \\ i &= i + w_{\text{input}} z_{\text{in}} \\ i &= i + w_{\text{rec}} z_{\text{rec}} \end{align*}\end{split}\]where \(z_{\text{rec}}\) and \(z_{\text{in}}\) are the recurrent and input spikes respectively.
- Parameters
input_size (int) – Size of the input.
hidden_size (int) – Size of the hidden state.
p (LIFExParameters) – Parameters of the LIF neuron model.
dt (float) – Time step to use.
a (bool) – Allow self-connections in the recurrence? Defaults to False.
Examples
>>> batch_size = 16 >>> lif_ex = LIFExRecurrentCell(10, 20) >>> input = torch.randn(batch_size, 10) >>> output, s0 = lif_ex(input)
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.LIFExState(z: torch.Tensor, v: torch.Tensor, i: torch.Tensor)[source]¶
Bases:
tupleState of a LIFEx neuron
- Parameters
z (torch.Tensor) – recurrent spikes
v (torch.Tensor) – membrane potential
i (torch.Tensor) – synaptic input current
Create new instance of LIFExState(z, v, i)
- i: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 2
- v: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 1
- z: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 0
- class norse.torch.module.LIFFeedForwardState(v: torch.Tensor, i: torch.Tensor)[source]¶
Bases:
tupleState of a feed forward LIF neuron
- Parameters
v (torch.Tensor) – membrane potential
i (torch.Tensor) – synaptic input current
Create new instance of LIFFeedForwardState(v, i)
- i: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 1
- v: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 0
- class norse.torch.module.LIFMCRecurrentCell(input_size, hidden_size, p=LIFParameters(tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=tensor(100.)), g_coupling=None, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNRecurrentCellComputes a single euler-integration step of a LIF multi-compartment neuron-model.
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} \dot{v} &= 1/\tau_{\text{mem}} (v_{\text{leak}} \ - g_{\text{coupling}} v + i) \\ \dot{i} &= -1/\tau_{\text{syn}} i \end{align*}\end{split}\]together with the jump condition
\[z = \Theta(v - v_{\text{th}})\]and transition equations
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} v &= (1-z) v + z v_{\text{reset}} \\ i &= i + w_{\text{input}} z_{\text{in}} \\ i &= i + w_{\text{rec}} z_{\text{rec}} \end{align*}\end{split}\]where \(z_{\text{rec}}\) and \(z_{\text{in}}\) are the recurrent and input spikes respectively.
- Parameters
input_size (int) – Size of the input. Also known as the number of input features.
hidden_size (int) – Size of the hidden state. Also known as the number of input features.
g_coupling (torch.Tensor) – conductances between the neuron compartments
p (LIFParameters) – neuron parameters
dt (float) – Integration timestep to use
autapses (bool) – Allow self-connections in the recurrence? Defaults to False.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- forward(input_tensor, state=None)[source]¶
Defines the computation performed at every call.
Should be overridden by all subclasses.
Note
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the
Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the registered hooks while the latter silently ignores them.
- class norse.torch.module.LIFMCRefracRecurrentCell(input_size, hidden_size, p=LIFRefracParameters(lif=LIFParameters(tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=tensor(100.)), rho_reset=tensor(5.)), g_coupling=None, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNRecurrentCellInitializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- forward(input_tensor, state=None)[source]¶
Defines the computation performed at every call.
Should be overridden by all subclasses.
Note
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the
Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the registered hooks while the latter silently ignores them.- Return type
- class norse.torch.module.LIFParameters(tau_syn_inv: torch.Tensor = tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv: torch.Tensor = tensor(100.), v_leak: torch.Tensor = tensor(0.), v_th: torch.Tensor = tensor(1.), v_reset: torch.Tensor = tensor(0.), method: str = 'super', alpha: float = tensor(100.))[source]¶
Bases:
tupleParametrization of a LIF neuron
- Parameters
tau_syn_inv (torch.Tensor) – inverse synaptic time constant (\(1/\tau_\text{syn}\)) in 1/ms
tau_mem_inv (torch.Tensor) – inverse membrane time constant (\(1/\tau_\text{mem}\)) in 1/ms
v_leak (torch.Tensor) – leak potential in mV
v_th (torch.Tensor) – threshold potential in mV
v_reset (torch.Tensor) – reset potential in mV
method (str) – method to determine the spike threshold (relevant for surrogate gradients)
alpha (float) – hyper parameter to use in surrogate gradient computation
Create new instance of LIFParameters(tau_syn_inv, tau_mem_inv, v_leak, v_th, v_reset, method, alpha)
- tau_mem_inv: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 1
- tau_syn_inv: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 0
- v_leak: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 2
- v_reset: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 4
- v_th: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 3
- class norse.torch.module.LIFRecurrent(input_size, hidden_size, p=LIFParameters(tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=tensor(100.)), **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNRecurrentA neuron layer that wraps a
LIFRecurrentCellin time such that the layer keeps track of temporal sequences of spikes. After application, the module returns a tuple containing(spikes from all timesteps, state from the last timestep).
Example
>>> data = torch.zeros(10, 5, 2) # 10 timesteps, 5 batches, 2 neurons >>> l = LIFRecurrent(2, 4) >>> l(data) # Returns tuple of (Tensor(10, 5, 4), LIFState)
- Parameters
input_size (int) – The number of input neurons
hidden_size (int) – The number of hidden neurons
p (LIFParameters) – The neuron parameters as a torch Module, which allows the module to configure neuron parameters as optimizable.
sparse (bool) – Whether to apply sparse activation functions (True) or not (False). Defaults to False.
input_weights (torch.Tensor) – Weights used for input tensors. Defaults to a random matrix normalized to the number of hidden neurons.
recurrent_weights (torch.Tensor) – Weights used for input tensors. Defaults to a random matrix normalized to the number of hidden neurons.
autapses (bool) – Allow self-connections in the recurrence? Defaults to False. Will also remove autapses in custom recurrent weights, if set above.
dt (float) – Time step to use in integration. Defaults to 0.001.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.LIFRecurrentCell(input_size, hidden_size, p=LIFParameters(tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=tensor(100.)), **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNRecurrentCellModule that computes a single euler-integration step of a leaky integrate-and-fire (LIF) neuron-model with recurrence but without time. More specifically it implements one integration step of the following ODE
\[\begin{align*} \dot{v} &= 1/\tau_{\text{mem}} (v_{\text{leak}} - v + i) \ \dot{i} &= -1/\tau_{\text{syn}} i \end{align*}\]together with the jump condition
\[z = \Theta(v - v_{\text{th}})\]and transition equations
\[\begin{align*} v &= (1-z) v + z v_{\text{reset}} \ i &= i + w_{\text{input}} z_{\text{in}} \ i &= i + w_{\text{rec}} z_{\text{rec}} \end{align*}\]where \(z_{\text{rec}}\) and \(z_{\text{in}}\) are the recurrent and input spikes respectively.
Example
>>> data = torch.zeros(5, 2) # 5 batches, 2 neurons >>> l = LIFRecurrentCell(2, 4) >>> l(data) # Returns tuple of (Tensor(5, 4), LIFState)
- Parameters
input_size (int) – Size of the input. Also known as the number of input features.
hidden_size (int) – Size of the hidden state. Also known as the number of input features.
p (LIFParameters) – Parameters of the LIF neuron model.
sparse (bool) – Whether to apply sparse activation functions (True) or not (False). Defaults to False.
input_weights (torch.Tensor) – Weights used for input tensors. Defaults to a random matrix normalized to the number of hidden neurons.
recurrent_weights (torch.Tensor) – Weights used for input tensors. Defaults to a random matrix normalized to the number of hidden neurons.
autapses (bool) – Allow self-connections in the recurrence? Defaults to False. Will also remove autapses in custom recurrent weights, if set above.
dt (float) – Time step to use.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.LIFRefracCell(p=LIFRefracParameters(lif=LIFParameters(tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=tensor(100.)), rho_reset=tensor(5.)), **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNCellModule that computes a single euler-integration step of a LIF neuron-model with absolute refractory period without recurrence. More specifically it implements one integration step of the following ODE.
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} \dot{v} &= 1/\tau_{\text{mem}} (1-\Theta(\rho)) (v_{\text{leak}} - v + i) \\ \dot{i} &= -1/\tau_{\text{syn}} i \\ \dot{\rho} &= -1/\tau_{\text{refrac}} \Theta(\rho) \end{align*}\end{split}\]together with the jump condition
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} z &= \Theta(v - v_{\text{th}}) \\ z_r &= \Theta(-\rho) \end{align*}\end{split}\]and transition equations
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} v &= (1-z) v + z v_{\text{reset}} \\ \rho &= \rho + z_r \rho_{\text{reset}} \end{align*}\end{split}\]- Parameters
p (LIFRefracParameters) – parameters of the lif neuron
dt (float) – Integration timestep to use
Examples
>>> batch_size = 16 >>> lif = LIFRefracCell() >>> input = torch.randn(batch_size, 20, 30) >>> output, s0 = lif(input)
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.LIFRefracFeedForwardState(lif: norse.torch.functional.lif.LIFFeedForwardState, rho: torch.Tensor)[source]¶
Bases:
tupleState of a feed forward LIF neuron with absolute refractory period.
- Parameters
lif (LIFFeedForwardState) – state of the feed forward LIF neuron integration
rho (torch.Tensor) – refractory state (count towards zero)
Create new instance of LIFRefracFeedForwardState(lif, rho)
- lif: norse.torch.functional.lif.LIFFeedForwardState¶
Alias for field number 0
- rho: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 1
- class norse.torch.module.LIFRefracParameters(lif: norse.torch.functional.lif.LIFParameters = LIFParameters(tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=tensor(100.)), rho_reset: torch.Tensor = tensor(5.))[source]¶
Bases:
tupleParameters of a LIF neuron with absolute refractory period.
- Parameters
lif (LIFParameters) – parameters of the LIF neuron integration
rho (torch.Tensor) – refractory state (count towards zero)
Create new instance of LIFRefracParameters(lif, rho_reset)
- lif: norse.torch.functional.lif.LIFParameters¶
Alias for field number 0
- rho_reset: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 1
- class norse.torch.module.LIFRefracRecurrentCell(input_size, hidden_size, p=LIFRefracParameters(lif=LIFParameters(tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=tensor(100.)), rho_reset=tensor(5.)), **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNRecurrentCellModule that computes a single euler-integration step of a LIF neuron-model with absolute refractory period. More specifically it implements one integration step of the following ODE.
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} \dot{v} &= 1/\tau_{\text{mem}} (1-\Theta(\rho)) (v_{\text{leak}} - v + i) \\ \dot{i} &= -1/\tau_{\text{syn}} i \\ \dot{\rho} &= -1/\tau_{\text{refrac}} \Theta(\rho) \end{align*}\end{split}\]together with the jump condition
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} z &= \Theta(v - v_{\text{th}}) \\ z_r &= \Theta(-\rho) \end{align*}\end{split}\]and transition equations
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} v &= (1-z) v + z v_{\text{reset}} \\ i &= i + w_{\text{input}} z_{\text{in}} \\ i &= i + w_{\text{rec}} z_{\text{rec}} \\ \rho &= \rho + z_r \rho_{\text{reset}} \end{align*}\end{split}\]where \(z_{\text{rec}}\) and \(z_{\text{in}}\) are the recurrent and input spikes respectively.
- Parameters
input_size (int) – Size of the input. Also known as the number of input features.
hidden_size (int) – Size of the hidden state. Also known as the number of input features.
p (LIFRefracParameters) – parameters of the lif neuron
dt (float) – Integration timestep to use
autapses (bool) – Allow self-connections in the recurrence? Defaults to False.
Examples
>>> batch_size = 16 >>> lif = LIFRefracRecurrentCell(10, 20) >>> input = torch.randn(batch_size, 10) >>> output, s0 = lif(input)
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.LIFRefracState(lif: norse.torch.functional.lif.LIFState, rho: torch.Tensor)[source]¶
Bases:
tupleState of a LIF neuron with absolute refractory period.
- Parameters
lif (LIFState) – state of the LIF neuron integration
rho (torch.Tensor) – refractory state (count towards zero)
Create new instance of LIFRefracState(lif, rho)
- lif: norse.torch.functional.lif.LIFState¶
Alias for field number 0
- rho: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 1
- class norse.torch.module.LIFState(z: torch.Tensor, v: torch.Tensor, i: torch.Tensor)[source]¶
Bases:
tupleState of a LIF neuron
- Parameters
z (torch.Tensor) – recurrent spikes
v (torch.Tensor) – membrane potential
i (torch.Tensor) – synaptic input current
Create new instance of LIFState(z, v, i)
- i: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 2
- v: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 1
- z: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 0
- class norse.torch.module.LILinearCell(input_size, hidden_size, p=LIParameters(tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.)), dt=0.001)[source]¶
Bases:
torch.nn.modules.module.ModuleCell for a leaky-integrator with an additional linear weighting. More specifically it implements a discretized version of the ODE
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} \dot{v} &= 1/\tau_{\text{mem}} (v_{\text{leak}} - v + i) \\ \dot{i} &= -1/\tau_{\text{syn}} i \end{align*}\end{split}\]and transition equations
\[i = i + w i_{\text{in}}\]- Parameters
input_size (int) – Size of the input. Also known as the number of input features.
hidden_size (int) – Size of the hidden state. Also known as the number of input features.
p (LIParameters) – parameters of the leaky integrator
dt (float) – integration timestep to use
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- forward(input_tensor, state=None)[source]¶
Defines the computation performed at every call.
Should be overridden by all subclasses.
Note
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the
Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the registered hooks while the latter silently ignores them.
- class norse.torch.module.LIParameters(tau_syn_inv: torch.Tensor = tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv: torch.Tensor = tensor(100.), v_leak: torch.Tensor = tensor(0.))[source]¶
Bases:
tupleParameters of a leaky integrator
- Parameters
tau_syn_inv (torch.Tensor) – inverse synaptic time constant
tau_mem_inv (torch.Tensor) – inverse membrane time constant
v_leak (torch.Tensor) – leak potential
Create new instance of LIParameters(tau_syn_inv, tau_mem_inv, v_leak)
- tau_mem_inv: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 1
- tau_syn_inv: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 0
- v_leak: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 2
- class norse.torch.module.LIState(v: torch.Tensor, i: torch.Tensor)[source]¶
Bases:
tupleState of a leaky-integrator
- Parameters
v (torch.Tensor) – membrane voltage
i (torch.Tensor) – input current
Create new instance of LIState(v, i)
- i: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 1
- v: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 0
- class norse.torch.module.LSNN(p=LSNNParameters(tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), tau_adapt_inv=tensor(0.0012), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), beta=tensor(1.8000), method='super', alpha=100.0), adjoint=False, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNA Long short-term memory neuron module without recurrence adapted from https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.09574
- Usage:
>>> from norse.torch import LSNN >>> layer = LSNN() >>> data = torch.zeros(5, 2) >>> output, state = layer.forward(data)
- Parameters
p (LSNNParameters) – The neuron parameters as a torch Module, which allows the module to configure neuron parameters as optimizable.
dt (float) – Time step to use in integration. Defaults to 0.001.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.LSNNCell(p=LSNNParameters(tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), tau_adapt_inv=tensor(0.0012), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), beta=tensor(1.8000), method='super', alpha=100.0), adjoint=False, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNCellEuler integration cell for LIF Neuron with threshold adaptation without recurrence. More specifically it implements one integration step of the following ODE
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} \dot{v} &= 1/\tau_{\text{mem}} (v_{\text{leak}} - v + i) \\ \dot{i} &= -1/\tau_{\\text{syn}} i \\ \dot{b} &= -1/\tau_{b} b \end{align*}\end{split}\]together with the jump condition
\[z = \Theta(v - v_{\text{th}} + b)\]and transition equations
\[\begin{split}\begin{align*} v &= (1-z) v + z v_{\text{reset}} \\ i &= i + \text{input} \\ b &= b + \beta z \end{align*}\end{split}\]- Parameters
p (torch.nn.Module) – parameters of the lsnn unit
p – The neuron parameters as a torch Module, which allows the module to configure neuron parameters as optimizable.
dt (float) – Time step to use in integration. Defaults to 0.001.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.LSNNFeedForwardState(v: torch.Tensor, i: torch.Tensor, b: torch.Tensor)[source]¶
Bases:
tupleIntegration state kept for a lsnn module
- Parameters
v (torch.Tensor) – membrane potential
i (torch.Tensor) – synaptic input current
b (torch.Tensor) – threshold adaptation
Create new instance of LSNNFeedForwardState(v, i, b)
- b: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 2
- i: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 1
- v: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 0
- class norse.torch.module.LSNNParameters(tau_syn_inv: torch.Tensor = tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv: torch.Tensor = tensor(100.), tau_adapt_inv: torch.Tensor = tensor(0.0012), v_leak: torch.Tensor = tensor(0.), v_th: torch.Tensor = tensor(1.), v_reset: torch.Tensor = tensor(0.), beta: torch.Tensor = tensor(1.8000), method: str = 'super', alpha: float = 100.0)[source]¶
Bases:
tupleParameters of an LSNN neuron
- Parameters
tau_syn_inv (torch.Tensor) – inverse synaptic time constant (\(1/\tau_\text{syn}\))
tau_mem_inv (torch.Tensor) – inverse membrane time constant (\(1/\tau_\text{mem}\))
tau_adapt_inv (torch.Tensor) – adaptation time constant (\(\tau_b\))
v_leak (torch.Tensor) – leak potential
v_th (torch.Tensor) – threshold potential
v_reset (torch.Tensor) – reset potential
beta (torch.Tensor) – adaptation constant
Create new instance of LSNNParameters(tau_syn_inv, tau_mem_inv, tau_adapt_inv, v_leak, v_th, v_reset, beta, method, alpha)
- beta: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 6
- tau_adapt_inv: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 2
- tau_mem_inv: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 1
- tau_syn_inv: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 0
- v_leak: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 3
- v_reset: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 5
- v_th: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 4
- class norse.torch.module.LSNNRecurrent(input_size, hidden_size, p=LSNNParameters(tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), tau_adapt_inv=tensor(0.0012), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), beta=tensor(1.8000), method='super', alpha=100.0), adjoint=False, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNRecurrentA Long short-term memory neuron module wit recurrence adapted from https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.09574
- Usage:
>>> from norse.torch.module import LSNNRecurrent >>> layer = LSNNRecurrent(2, 10) // Shape 2 -> 10 >>> data = torch.zeros(2, 5, 2) // Arbitrary data >>> output, state = layer.forward(data) // Out: (2, 5, 10)
- Parameters
input_size (int) – Size of the input. Also known as the number of input features.
hidden_size (int) – Size of the hidden state. Also known as the number of input features.
p (LSNNParameters) – The neuron parameters as a torch Module, which allows the module to configure neuron parameters as optimizable.
dt (float) – Time step to use in integration. Defaults to 0.001.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.LSNNRecurrentCell(input_size, hidden_size, p=LSNNParameters(tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), tau_adapt_inv=tensor(0.0012), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), beta=tensor(1.8000), method='super', alpha=100.0), adjoint=False, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
norse.torch.module.snn.SNNRecurrentCellModule that computes a single euler-integration step of a LSNN neuron-model with recurrence. More specifically it implements one integration step of the following ODE
\[\begin{split}\\begin{align*} \dot{v} &= 1/\\tau_{\\text{mem}} (v_{\\text{leak}} - v + i) \\\\ \dot{i} &= -1/\\tau_{\\text{syn}} i \\\\ \dot{b} &= -1/\\tau_{b} b \end{align*}\end{split}\]together with the jump condition
\[\begin{split}z = \Theta(v - v_{\\text{th}} + b)\end{split}\]and transition equations
\[\begin{split}\\begin{align*} v &= (1-z) v + z v_{\\text{reset}} \\\\ i &= i + w_{\\text{input}} z_{\\text{in}} \\\\ i &= i + w_{\\text{rec}} z_{\\text{rec}} \\\\ b &= b + \\beta z \end{align*}\end{split}\]where \(z_{\\text{rec}}\) and \(z_{\\text{in}}\) are the recurrent and input spikes respectively.
- Parameters
input_size (int) – Size of the input. Also known as the number of input features.
hidden_size (int) – Size of the hidden state. Also known as the number of input features.
p (LSNNParameters) – parameters of the lsnn unit
dt (float) – Integration timestep to use
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class norse.torch.module.LSNNState(z: torch.Tensor, v: torch.Tensor, i: torch.Tensor, b: torch.Tensor)[source]¶
Bases:
tupleState of an LSNN neuron
- Parameters
z (torch.Tensor) – recurrent spikes
v (torch.Tensor) – membrane potential
i (torch.Tensor) – synaptic input current
b (torch.Tensor) – threshold adaptation
Create new instance of LSNNState(z, v, i, b)
- b: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 3
- i: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 2
- v: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 1
- z: torch.Tensor¶
Alias for field number 0
- class norse.torch.module.Lift(module)[source]¶
Bases:
torch.nn.modules.module.Module- Lift applies a given torch.nn.Module over
a temporal sequence. In other words this module applies the given torch.nn.Module N times, where N is the outer dimension in the provided tensor.
- Parameters
module (
Module) – Module to apply
Examples
>>> batch_size = 16 >>> seq_length = 1000 >>> in_channels = 64 >>> out_channels = 32 >>> conv2d = Lift(torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 5, 1)) >>> data = torch.randn(seq_length, batch_size, 20, 30) >>> output = conv2d(data)
>>> data = torch.randn(seq_length, batch_size, in_channels, 20, 30) >>> module = torch.nn.Sequential( >>> Lift(torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 5, 1)), >>> LIF(), >>> ) >>> output, _ = module(data)
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- forward(x)[source]¶
Apply the module over the input along the 0-th (time) dimension and accumulate the outputs in an output tensor.
- Parameters
x (
Union[Tensor,Tuple[Tensor,Tensor]]) – Union[torch.Tensor, Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]]
Note
If the input is a tuple of two tensors, the second tuple entry will be ignored.
- Return type
- class norse.torch.module.PoissonEncoder(seq_length, f_max=100, dt=0.001)[source]¶
Bases:
torch.nn.modules.module.ModuleEncodes a tensor of input values, which are assumed to be in the range [0,1] into a tensor of one dimension higher of binary values, which represent input spikes.
- Parameters
- forward(x)[source]¶
Defines the computation performed at every call.
Should be overridden by all subclasses.
Note
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the
Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the registered hooks while the latter silently ignores them.
- class norse.torch.module.PopulationEncoder(out_features, scale=None, kernel=<function gaussian_rbf>, distance_function=<function euclidean_distance>)[source]¶
Bases:
torch.nn.modules.module.ModuleEncodes a set of input values into population codes, such that each singular input value is represented by a list of numbers (typically calculated by a radial basis kernel), whose length is equal to the out_features.
Population encoding can be visualised by imagining a number of neurons in a list, whose activity increases if a number gets close to its “receptive field”.
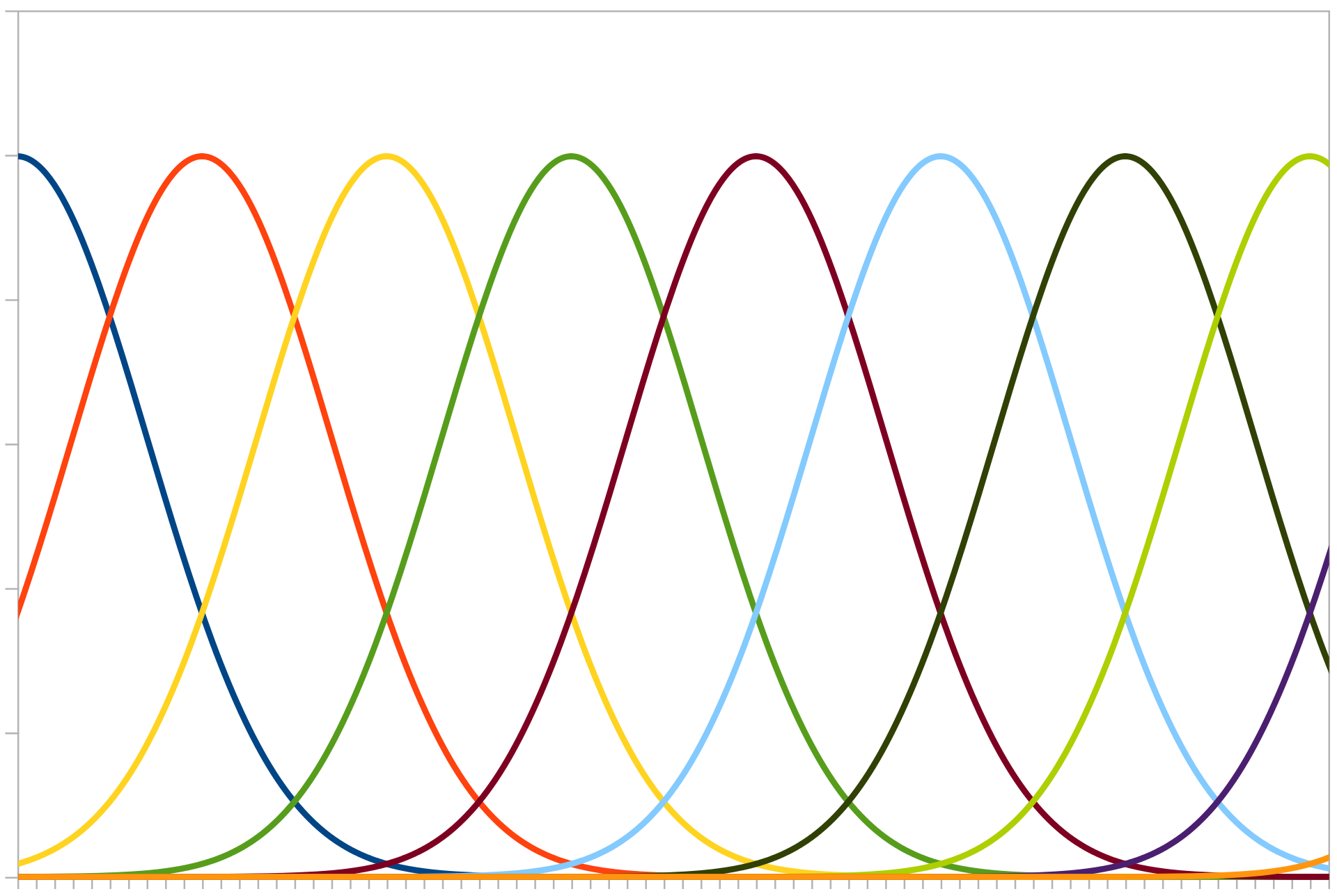
Gaussian curves representing different neuron “receptive fields”. Image credit: Andrew K. Richardson.¶
super(PopulationEncoder, self).__init__()mons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:PopulationCode.svg
Example
>>> data = torch.as_tensor([0, 0.5, 1]) >>> out_features = 3 >>> PopulationEncoder(out_features).forward(data) tensor([[1.0000, 0.8825, 0.6065], [0.8825, 1.0000, 0.8825], [0.6065, 0.8825, 1.0000]])
- Parameters
out_features (int) – The number of output per input value
scale (torch.Tensor) – The scaling factor for the kernels. Defaults to the maximum value of the input. Can also be set for each individual sample.
kernel (
Callable[[Tensor],Tensor]) – A function that takes two inputs and returns a tensor. The two inputs represent the center value (which changes for each index in the output tensor) and the actual data value to encode respectively.z Defaults to gaussian radial basis kernel function.distance_function (
Callable[[Tensor,Tensor],Tensor]) – A function that calculates the distance between two numbers. Defaults to euclidean.
- forward(input_tensor)[source]¶
Defines the computation performed at every call.
Should be overridden by all subclasses.
Note
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the
Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the registered hooks while the latter silently ignores them.
- class norse.torch.module.RegularizationCell(accumulator=<function spike_accumulator>, state=None)[source]¶
Bases:
torch.nn.modules.module.ModuleA regularisation cell that accumulates some state (for instance number of spikes) for each forward step, which can later be applied to a loss term.
Example
>>> import torch >>> from norse.torch.module import lif, regularization >>> cell = lif.LIFCell(2, 4) # 2 -> 4 >>> r = regularization.RegularizationCell() # Defaults to spike counting >>> data = torch.ones(5, 2) # Batch size of 5 >>> z, s = cell(data) >>> z, regularization_term = r(z, s) >>> ... >>> loss = ... + 1e-3 * regularization_term
- Parameters
accumulator (Accumulator) – The accumulator that aggregates some data (such as spikes) that can later be included in an error term.
state (Optional[T]) – The regularization state to be aggregated to of any type T. Defaults to None.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- forward(z, s)[source]¶
Defines the computation performed at every call.
Should be overridden by all subclasses.
Note
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the
Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the registered hooks while the latter silently ignores them.
- class norse.torch.module.SequentialState(*args)[source]¶
Bases:
torch.nn.modules.container.SequentialA sequential model that works like PyTorch’s
Sequentialwith the addition that it handles neuron states.- Parameters
args (*torch.nn.Module) – A list of modules to sequentially apply in the forward pass
Example
>>> import torch >>> import norse.torch as snn >>> data = torch.ones(1, 16, 8, 4) # Single timestep >>> model = snn.SequentialState( >>> snn.Lift(torch.nn.Conv2d(16, 8, 3)), # (1, 8, 6, 2) >>> torch.nn.Flatten(2), # (1, 8, 12) >>> snn.LIFRecurrent(12, 6), # (1, 8, 6) >>> snn.LIFRecurrent(6, 1) # (1, 8, 1) >>> ) >>> model(data)
- Example with recurrent layers:
>>> import torch >>> import norse.torch as snn >>> data = torch.ones(1, 16, 8, 4) # Single timestep >>> model = snn.SequentialState( >>> snn.Lift(torch.nn.Conv2d(16, 8, 3)), # (1, 8, 6, 2) >>> torch.nn.Flatten(2), # (1, 8, 12) >>> snn.LSNNRecurrent(12, 6), # (1, 8, 6) >>> torch.nn.RNN(6, 4, 2), # (1, 6, 4) with 2 recurrent layers >>> snn.LIFRecurrent(4, 1) # (1, 4, 1) >>> ) >>> model(data)
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- forward(input_tensor, state=None)[source]¶
Feeds the input to the modules with the given state-list. If the state is None, the initial state is set to None for each of the modules.
- register_forward_state_hooks(forward_hook)[source]¶
Registers hooks for all state*ful* layers.
Hooks can be removed by calling :meth:`remove_state_hooks`_.
- Parameters
child_hook (Callable) – The hook applied to all children everytime they produce an output
pre_hook (Optional[Callable]) – An optional hook for the SequentialState module, executed before the input is propagated to the children.
Example
>>> import norse.torch as snn >>> def my_hook(module, input, output): >>> ... >>> module = snn.SequentialState(...) >>> module.register_forward_state_hook(my_hook) >>> module(...)
- remove_forward_state_hooks()[source]¶
Disables the forward state hooks, registered in :meth:`register_forward_state_hooks`_.
- class norse.torch.module.SignedPoissonEncoder(seq_length, f_max=100, dt=0.001)[source]¶
Bases:
torch.nn.modules.module.ModuleEncodes a tensor of input values, which are assumed to be in the range [-1,1] into a tensor of one dimension higher of values in {-1,0,1}, which represent signed input spikes.
- Parameters
- forward(x)[source]¶
Defines the computation performed at every call.
Should be overridden by all subclasses.
Note
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the
Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the registered hooks while the latter silently ignores them.
- class norse.torch.module.SpikeLatencyEncoder[source]¶
Bases:
torch.nn.modules.module.ModuleFor all neurons, remove all but the first spike. This encoding basically measures the time it takes for a neuron to spike first. Assuming that the inputs are constant, this makes sense in that strong inputs spikes fast.
Spikes are identified by their unique position in the input array.
Example
>>> data = torch.as_tensor([[0, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1]]) >>> encoder = torch.nn.Sequential( ConstantCurrentLIFEncoder() SpikeLatencyEncoder() ) >>> encoder(data) tensor([[0, 1, 1], [1, 0, 0]])
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- forward(input_spikes)[source]¶
Defines the computation performed at every call.
Should be overridden by all subclasses.
Note
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the
Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the registered hooks while the latter silently ignores them.
- class norse.torch.module.SpikeLatencyLIFEncoder(seq_length, p=LIFParameters(tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=tensor(100.)), dt=0.001)[source]¶
Bases:
torch.nn.modules.module.ModuleEncodes an input value by the time the first spike occurs. Similar to the ConstantCurrentLIFEncoder, but the LIF can be thought to have an infinite refractory period.
- Parameters
sequence_length (int) – Number of time steps in the resulting spike train.
p (LIFParameters) – Parameters of the LIF neuron model.
dt (float) – Integration time step (should coincide with the integration time step used in the model)
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- forward(input_current)[source]¶
Defines the computation performed at every call.
Should be overridden by all subclasses.
Note
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the
Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the registered hooks while the latter silently ignores them.
Subpackages¶
- norse.torch.module.test package
- Submodules
- norse.torch.module.test.test_coba module
- norse.torch.module.test.test_conv module
- norse.torch.module.test.test_encode module
- norse.torch.module.test.test_izhikevich module
- norse.torch.module.test.test_leaky_integrator module
- norse.torch.module.test.test_lif module
- norse.torch.module.test.test_lif_adex module
- norse.torch.module.test.test_lif_correlation module
- norse.torch.module.test.test_lif_ex module
- norse.torch.module.test.test_lif_mc module
- norse.torch.module.test.test_lif_mc_refrac module
- norse.torch.module.test.test_lif_refrac module
- norse.torch.module.test.test_lift module
- norse.torch.module.test.test_lsnn module
- norse.torch.module.test.test_regularization module
- norse.torch.module.test.test_sequential module
- norse.torch.module.test.test_snn module
- norse.torch.module.test.test_training module
- Submodules
Submodules¶
- norse.torch.module.coba_lif module
- norse.torch.module.conv module
- norse.torch.module.encode module
- norse.torch.module.izhikevich module
- norse.torch.module.leaky_integrator module
- norse.torch.module.lif module
- norse.torch.module.lif_adex module
- norse.torch.module.lif_correlation module
- norse.torch.module.lif_ex module
- norse.torch.module.lif_mc module
- norse.torch.module.lif_mc_refrac module
- norse.torch.module.lif_refrac module
- norse.torch.module.lift module
- norse.torch.module.lsnn module
- norse.torch.module.regularization module
- norse.torch.module.sequential module
- norse.torch.module.snn module
