norse.torch.functional.encode module¶
Stateless encoding functionality for Norse, offering different ways to convert numerical inputs to the spiking domain. Note that some functions, like population_encode does not return spikes, but rather numerical values that will have to be converted into spikes via, for instance, the poisson encoder.
- norse.torch.functional.encode.constant_current_lif_encode(input_current, seq_length, p=LIFParameters(tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=tensor(100.)), dt=0.001)[source]¶
Encodes input currents as fixed (constant) voltage currents, and simulates the spikes that occur during a number of timesteps/iterations (seq_length).
Example
>>> data = torch.as_tensor([2, 4, 8, 16]) >>> seq_length = 2 # Simulate two iterations >>> constant_current_lif_encode(data, seq_length) # State in terms of membrane voltage (tensor([[0.2000, 0.4000, 0.8000, 0.0000], [0.3800, 0.7600, 0.0000, 0.0000]]), # Spikes for each iteration tensor([[0., 0., 0., 1.], [0., 0., 1., 1.]]))
- Parameters
input_current (torch.Tensor) – The input tensor, representing LIF current
seq_length (int) – The number of iterations to simulate
p (LIFParameters) – Initial neuron parameters.
dt (float) – Time delta between simulation steps
- Return type
- Returns
A tensor with an extra dimension of size seq_length containing spikes (1) or no spikes (0).
- norse.torch.functional.encode.gaussian_rbf(tensor, sigma=1)[source]¶
A gaussian radial basis kernel that calculates the radial basis given a distance value (distance between \(x\) and a data value \(x'\), or \(\|\mathbf{x} - \mathbf{x'}\|^2\) below).
\[K(\mathbf{x}, \mathbf{x'}) = \exp\left(- \frac{\|\mathbf{x} - \mathbf{x'}\|^2}{2\sigma^2}\right)\]- Parameters
tensor (torch.Tensor) – The tensor containing distance values to convert to radial bases
sigma (float) – The spread of the gaussian distribution. Defaults to 1.
- norse.torch.functional.encode.poisson_encode(input_values, seq_length, f_max=100, dt=0.001)[source]¶
Encodes a tensor of input values, which are assumed to be in the range [0,1] into a tensor of one dimension higher of binary values, which represent input spikes.
See for example https://www.cns.nyu.edu/~david/handouts/poisson.pdf.
- Parameters
input_values (torch.Tensor) – Input data tensor with values assumed to be in the interval [0,1].
sequence_length (int) – Number of time steps in the resulting spike train.
f_max (float) – Maximal frequency (in Hertz) which will be emitted.
dt (float) – Integration time step (should coincide with the integration time step used in the model)
- Return type
- Returns
A tensor with an extra dimension of size seq_length containing spikes (1) or no spikes (0).
- norse.torch.functional.encode.poisson_encode_step(input_values, f_max=1000, dt=0.001)[source]¶
Encodes a tensor of input values, which are assumed to be in the range [0,1] into a tensor of binary values, which represent input spikes.
See for example https://www.cns.nyu.edu/~david/handouts/poisson.pdf.
- Parameters
input_values (torch.Tensor) – Input data tensor with values assumed to be in the interval [0,1].
f_max (float) – Maximal frequency (in Hertz) which will be emitted.
dt (float) – Integration time step (should coincide with the integration time step used in the model)
- Return type
- Returns
A tensor containing binary values in .
- norse.torch.functional.encode.population_encode(input_values, out_features, scale=None, kernel=<function gaussian_rbf>, distance_function=<function euclidean_distance>)[source]¶
Encodes a set of input values into population codes, such that each singular input value is represented by a list of numbers (typically calculated by a radial basis kernel), whose length is equal to the out_features.
Population encoding can be visualised by imagining a number of neurons in a list, whose activity increases if a number gets close to its “receptive field”.
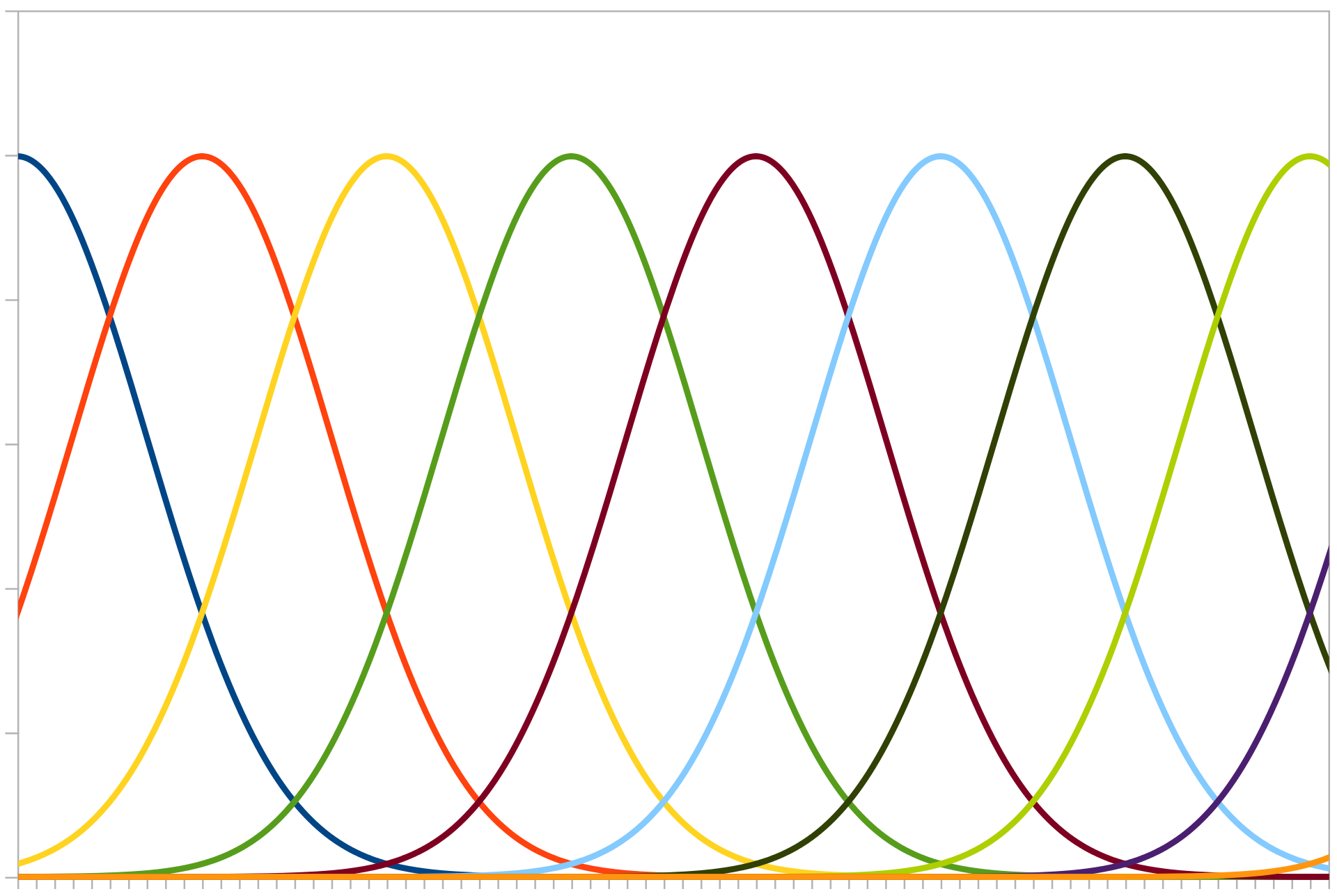
Gaussian curves representing different neuron “receptive fields”. Image credit: Andrew K. Richardson.¶
Example
>>> data = torch.as_tensor([0, 0.5, 1]) >>> out_features = 3 >>> pop_encoded = population_encode(data, out_features) tensor([[1.0000, 0.8825, 0.6065], [0.8825, 1.0000, 0.8825], [0.6065, 0.8825, 1.0000]]) >>> spikes = poisson_encode(pop_encoded, 1).squeeze() # Convert to spikes
- Parameters
input_values (torch.Tensor) – The input data as numerical values to be encoded to population codes
out_features (int) – The number of output per input value
scale (torch.Tensor) – The scaling factor for the kernels. Defaults to the maximum value of the input. Can also be set for each individual sample.
kernel (
Callable[[Tensor],Tensor]) – A function that takes two inputs and returns a tensor. The two inputs represent the center value (which changes for each index in the output tensor) and the actual data value to encode respectively.z Defaults to gaussian radial basis kernel function.distance_function (
Callable[[Tensor,Tensor],Tensor]) – A function that calculates the distance between two numbers. Defaults to euclidean.
- Return type
- Returns
A tensor with an extra dimension of size seq_length containing population encoded values of the input stimulus. Note: An extra step is required to convert the values to spikes, see above.
- norse.torch.functional.encode.signed_poisson_encode(input_values, seq_length, f_max=100, dt=0.001)[source]¶
Encodes a tensor of input values, which are assumed to be in the range [-1,1] into a tensor of one dimension higher of binary values, which represent input spikes.
- Parameters
input_values (torch.Tensor) – Input data tensor with values assumed to be in the interval [-1,1].
sequence_length (int) – Number of time steps in the resulting spike train.
f_max (float) – Maximal frequency (in Hertz) which will be emitted.
dt (float) – Integration time step (should coincide with the integration time step used in the model)
- Return type
- Returns
A tensor with an extra dimension of size seq_length containing values in {-1,0,1}
- norse.torch.functional.encode.signed_poisson_encode_step(input_values, f_max=1000, dt=0.001)[source]¶
Creates a poisson distributed signed spike vector, when
- Parameters
input_values (torch.Tensor) – Input data tensor with values assumed to be in the interval [-1,1].
f_max (float) – Maximal frequency (in Hertz) which will be emitted.
dt (float) – Integration time step (should coincide with the integration time step used in the model)
- Return type
- Returns
A tensor containing values in {-1,0,1}.
- norse.torch.functional.encode.spike_latency_encode(input_spikes)[source]¶
For all neurons, remove all but the first spike. This encoding basically measures the time it takes for a neuron to spike first. Assuming that the inputs are constant, this makes sense in that strong inputs spikes fast.
Spikes are identified by their unique position within each sequence.
Example
>>> data = torch.as_tensor([[0, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1]]) >>> spike_latency_encode(data) tensor([[0, 1, 1], [1, 0, 0]])
- Parameters
input_spikes (torch.Tensor) – A tensor of input spikes, assumed to be at least 2D (sequences, …)
- Return type
- Returns
A tensor where the first spike (1) is retained in the sequence
- norse.torch.functional.encode.spike_latency_lif_encode(input_current, seq_length, p=LIFParameters(tau_syn_inv=tensor(200.), tau_mem_inv=tensor(100.), v_leak=tensor(0.), v_th=tensor(1.), v_reset=tensor(0.), method='super', alpha=tensor(100.)), dt=0.001)[source]¶
Encodes an input value by the time the first spike occurs. Similar to the ConstantCurrentLIFEncoder, but the LIF can be thought to have an infinite refractory period.
- Parameters
input_current (torch.Tensor) – Input current to encode (needs to be positive).
sequence_length (int) – Number of time steps in the resulting spike train.
p (LIFParameters) – Parameters of the LIF neuron model.
dt (float) – Integration time step (should coincide with the integration time step used in the model)
- Return type
